Design and Synthesis of Shikimoylated-Polypeptides for Nuclear Specific Internalization
- Feb 9, 2022
- 1 min read
ACS Macro Lett. 2022, 11, 3, 289–295
Abstract
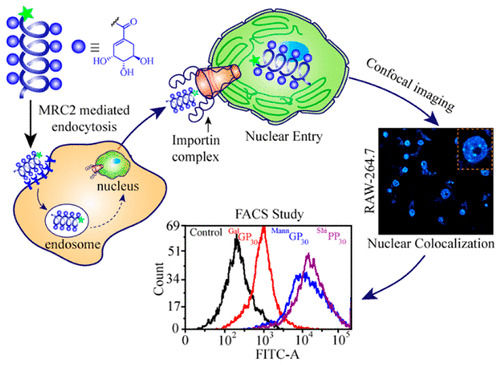
Targeted delivery of therapeutics such as small molecule drugs or nucleic acids exclusively to the nucleus of diseased mammalian cells poses a significant challenge. The development of targeting ligands that can specifically enter certain cancer cells via a specific receptor-mediated endocytosis and then traffic exclusively to the nucleus to deliver the cargo inside it can achieve this goal. We have developed an end-functionalized shikimoylated-polypeptide with pendant shikimoyl moieties that can enter mammalian cells via the mannose receptors and are then exclusively trafficked into the nucleus. The presence of the shikimoyl group in the polypeptide, which traffics it exclusively to the nucleus, contrasts with the mannosylated or galactosylated glycopolypeptides that are distributed all over the cytoplasm or the mannose-6-phosphate containing polypeptide that is exclusively trafficked to the lysosome. Using challenge experiments, we demonstrate that these polypeptides can enter both dendritic and cancer cells through mannose-receptors and subsequently enter the cell nucleus via the interaction with a nuclear pore complex (NPC) protein importin-α/β1. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the first example of a synthetic polyvalent glycopolypeptide mimic that performs the dual function of entering mammalian cells through specific receptors and subsequently traffics into the nucleus. The conjugation of these end-functionalized shikimoylated-polypeptides to other biological entities, such as recombinant anticancer drugs, DNA, RNA, and CRISPR-Cas9, may be a suitable alternative for delivery of these biological entities into cells affected by cancer and other genetic diseases.

Comments